Java集合框架笔记01--Collection基础概念; List及实现类
Java集合框架笔记01
基础概念
- 集合: 对象的容器,实现了对 对象 常用的操作,类似数组的功能。
- 集合与数组的区别:
- 数组长度固定,集合长度不固定。
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型
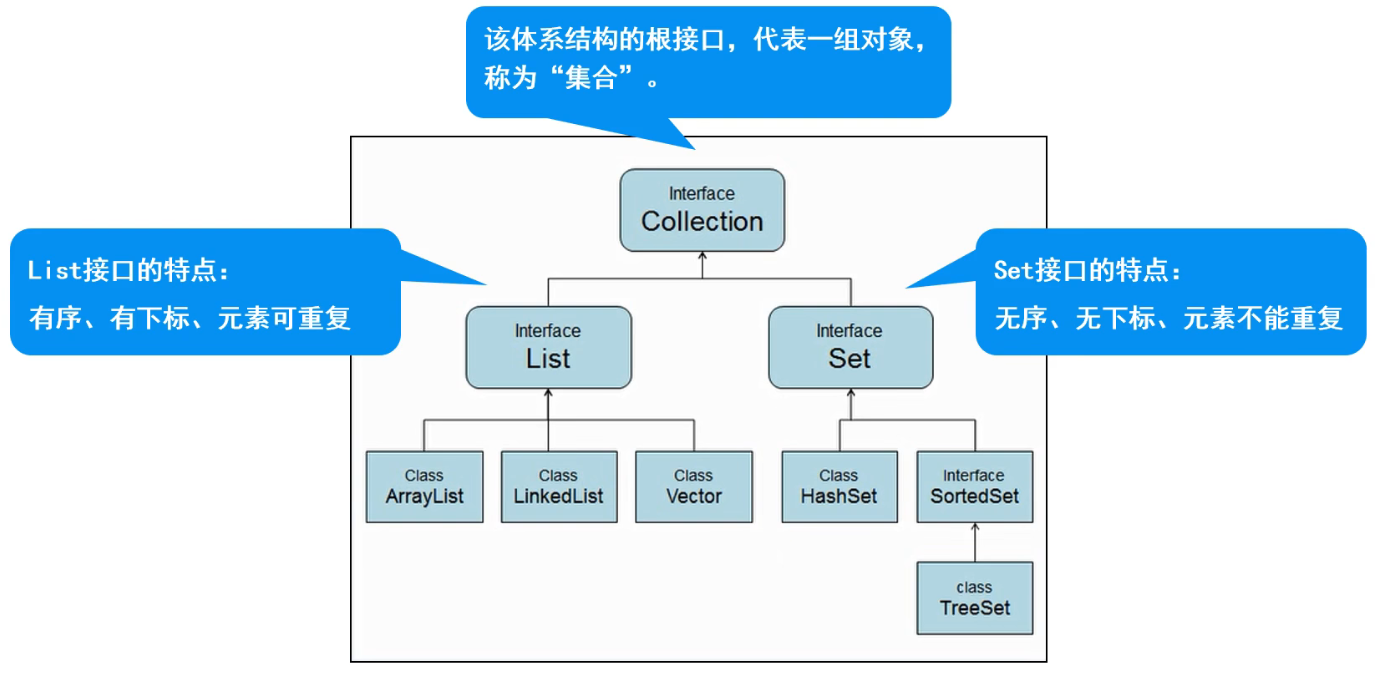
Collection体系集合
Collection体系集合框架:
 `
`Collection父接口
方法:
- boolean add(E e) // 添加一个元素
- boolean addAll(Collection c) // 将集合c中的所有元素添加到此集合
- void clear() // 清空集合中的所有元素
- boolean contains(Object o) // 检查集合中是否包含o元素
- boolean containsAll(Collection c) // 检查集合中是否包含c中所有元素
- boolean equals(Object obj) // equals
- boolean isEmpty() // 判断集合是否为空集合
- boolean remove(Object o) // 移除o元素
- boolean removeAll(Collection c) // 移除也包含在集合c中的所有元素
- boolean retainAll(Collection c) // 相当于交集,仅此集合中保留也包含在c中的元素
- int size() // 返回集合中的元素的个数
- Object[] toArray() // 将集合转换成数组
遍历Collection:
增强for (for-each)
迭代器(Iterator)
(1)有三个方法:
- hasNext(); // 有没有下一个元素
- next(); // 获取下一个元素
- remove(); // 删除一个元素
(2)使用迭代器遍历集合的典型代码段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String s = (String) it.next();
System.out.println(s);
/*
* !!! 不允许遍历过程中使用Collection中的其他方法改变集合中的元素 !!!
* 否则将抛出“ConcurrentModificationException” 并发修改异常
* 但可以使用迭代器中的remove()方法删除元素
*/
// collection.remove(s); // 不允许! 抛出ConcurrentModificationException异常
// it.remove(); // 允许
}
List子接口
特点:
有序、有下标、元素可重复
方法:
包含Collection父接口中的全部方法,并包含以下方法:
- void add(int index, E element) // 将元素插入指定位置
- boolean addAll(int index, Collection c) // 将c中的所有元素插入到此集合的指定位置
- E get(int index) // 获取指定位置的元素
- List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) // 截取部分列表
- indexOf(Object o) // 获取o第一次出现的位置
- lastIndexOf(Object o) //
- remove(int index)
遍历方式:
可以使用for、增强for、迭代器遍历
ListIterator:
比Collection的Iterator功能更强大,既可以前向遍历,又可以后向遍历,还可以在遍历过程中添加、修改或删除元素。
包含以下方法:
- void add(E e) // 将e插入list
- boolean hasNext()
- boolean hasPrevious()
- E next() // 返回下一个元素并移动游标
- int nextIndex() // 返回下个元素的下标
- E previous()
- int previousIndex()
- void remove() // 删除上一次调用next或previous返回的元素
- void set(E e) // 修改上一次调用next或previous返回的元素
List的实现类:
- ArrayList
- 数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢
- 运行效率快、线程不安全
- Vector
- 数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢
- 运行效率慢、线程安全
- LinkedList
- 链表结构实现,增删快、查询慢
- ArrayList
ArrayList 源码分析
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 默认容量大小
-- 如果没有像集合中添加任何元素时,容量是0;添加一个元素之后,容量是10
elementData 存放元素的数组
size 实际元素个数
add方法,在数组容量不够时,扩容为原来的1.5倍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}LinkedList 源码分析
基于双向链表
int size 集合大小
Node first 链表的头节点
Node last 链表的尾节点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!